List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 204 goods from 82 countries and areas, as of September 5, 2024.
The Frederick Douglass Trafficking Victims Prevention and Protection Reauthorization Act of 2018 directs that the List include, "to the extent practicable, goods that are produced with inputs that are produced with forced labor or child labor."
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Previous TVPRA List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
2022
- List of Downstream Goods (Excel)
- List of Goods (Bibliography) (PDF)
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
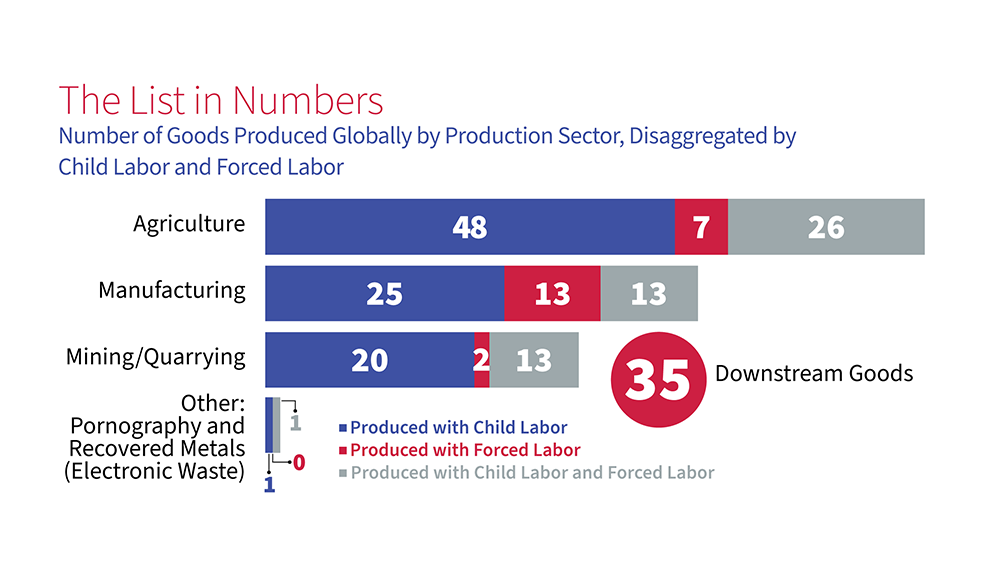
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
DOL's mission is to foster, promote, and develop the welfare of the wage earners, job seekers, and retirees of the United States. This DOL mission is carried out by a variety of sub-agencies and offices (DOL agencies) covering domestic and international policy engagements, workforce development, enforcement, statistics, and benefits. DOL has a responsibility to protect the integrity of scientific information that is produced, communicated, and used across DOL agencies to better carry out its mission. ILAB is committed to using the highest possible scientific integrity and quality standards and practices to conduct our critical work. Scientific integrity is the adherence to professional practices, ethical behavior, and the principles of honesty and objectivity when conducting, managing, using the results of, and communicating about science and scientific activities. Inclusivity, transparency, and protection from inappropriate influence are hallmarks of scientific integrity.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Pakistan | There is evidence that children under the age of 14 produce baked goods in Pakistan. An analysis of the Pakistan Labour Force Survey 2017–2018 considers all work performed by children under age 14 to be child labor. Based on an analysis of the survey, it is estimated that 15,404 child laborers produce baked goods. Children who work in producing baked goods may be at risk of exposure to hazards including working long hours, carrying heavy loads, and exposure to extreme temperatures and toxic fumes. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Pakistan’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgment that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Burma | There are reports that children as young as age 10 are forced to work in the production of bamboo in Burma. According to the ILO and NGOs, forced child labor is pervasive, particularly in Karen, Shan, and Arakan States near military camps, with children constituting up to 40 percent of forced laborers being used for a variety of activities, including the production of bamboo. Some of these children are sent by their families to fulfill a mandate imposed by the military that requires each household in a village to undertake specified forced labor activities. Villagers, including children, are forced by local officials and the military to work cutting bamboo for the military camps. The forced child laborers are not paid for their work, and face physical violence or other punishment if they refuse to work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Belize | Child Labor | |
| Brazil | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 13 cultivate bananas in Brazil. The Government of Brazil’s 2015 National Household Survey considers all work performed by children below age 14 to be child labor. Based on an analysis of the survey, an estimated 2,936 child laborers cultivate bananas. The ILO has found that generally children who work in agriculture may be at risk of exposure to hazards including, working long hours, carrying heavy loads, using dangerous tools, and exposure to the elements, physical injuries, and chemicals, such as pesticides. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Brazil’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Ecuador | Child Labor | |
| Nicaragua | Child Labor | |
| Philippines | Child Labor | |
| Paraguay | There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 grow beans in Paraguay. In 2016, the Government of Paraguay published representative results from the Survey of Activities of Rural Area Children and Adolescents 2015. The survey considers a working child to be engaged in child labor if the child is below the minimum age for employment of 14 or is performing work that is hazardous according to national legislation. The survey estimates that 301,827 children ages 5 to 17 perform hazardous work in rural areas of Paraguay and indicates that children working in agriculture experience accidents and illnesses, including from using dangerous tools and handling chemicals. According to the survey, almost 13 percent of Paraguayan children engaged in child labor in agriculture do not attend school. The survey estimates that 71,839 child laborers grow poroto beans throughout rural areas in Paraguay. Approximately 31,372 of child laborers growing poroto beans are below the minimum age for employment in Paraguay. The survey indicates that child labor also occurs in the cultivation of other varieties of beans, including habilla, poroto manteca, and feijao, and that more boys than girls are engaged in child labor producing beans. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Paraguay’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Mexico | Child Labor | |
| Burma | There are reports that children ages 15-17 work under conditions of forced labor in the production of beans in Burma. An NGO study documents children, as well as adults, forced by the military to work on rotation year round, planting and harvesting beans for the military camp. Local officials and the military enforce these work orders; the children cannot refuse to work, even if sick. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?