List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 204 goods from 82 countries and areas, as of September 5, 2024.
The Frederick Douglass Trafficking Victims Prevention and Protection Reauthorization Act of 2018 directs that the List include, "to the extent practicable, goods that are produced with inputs that are produced with forced labor or child labor."
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Previous TVPRA List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
2022
- List of Downstream Goods (Excel)
- List of Goods (Bibliography) (PDF)
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
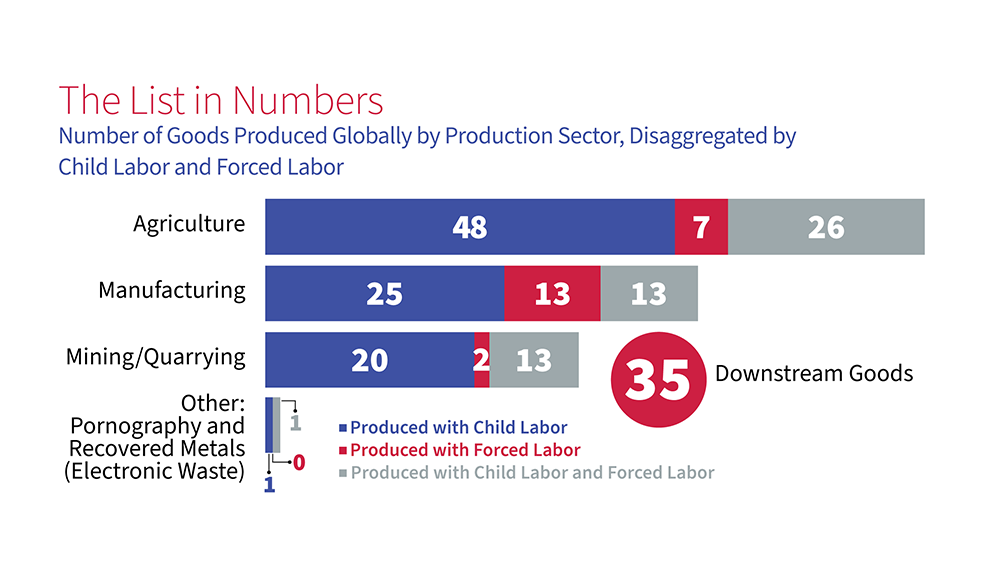
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
DOL's mission is to foster, promote, and develop the welfare of the wage earners, job seekers, and retirees of the United States. This DOL mission is carried out by a variety of sub-agencies and offices (DOL agencies) covering domestic and international policy engagements, workforce development, enforcement, statistics, and benefits. DOL has a responsibility to protect the integrity of scientific information that is produced, communicated, and used across DOL agencies to better carry out its mission. ILAB is committed to using the highest possible scientific integrity and quality standards and practices to conduct our critical work. Scientific integrity is the adherence to professional practices, ethical behavior, and the principles of honesty and objectivity when conducting, managing, using the results of, and communicating about science and scientific activities. Inclusivity, transparency, and protection from inappropriate influence are hallmarks of scientific integrity.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Côte d'Ivoire | There are reports that children from within Côte d'Ivoire, as well as migrant children from Benin, Burkina Faso, Guinea, Mali, Nigeria, and Togo, are working under conditions of forced labor on Ivoirian cocoa farms. Based on the most recently available estimate from Tulane University, over 4,000 children work in conditions of forced labor in the production of cocoa in Côte d'Ivoire. Some children are sold by their parents to traffickers, some are kidnapped, and others migrate willingly but fall victim to traffickers who sell them to recruiters or farmers, where they end up in conditions of bonded labor. Some farmers buy the children and refuse to let them leave the farm until the debt of their purchase has been worked off. The children are frequently not paid for their work; some of their wages are paid to the recruiter or trafficker. These children are held against their will on isolated farms, are locked in their living quarters at night, and are threatened and beaten if they attempt to escape. They are punished by their employers with physical abuse. They are forced to work long hours, including overtime, and are required to work even when they are sick. Some children are denied sufficient food by their traffickers and employers. Some children are forced to perform dangerous tasks, including carrying heavy loads, using machetes and sharp tools, and applying pesticides and fertilizers. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Ghana | Child Labor | |
| Guinea | Child Labor | |
| Nigeria | There are reports that children are forced to produce cocoa in Nigeria. The ILO, media pieces, and an academic report indicate that children are trafficked across Nigeria and from Burkina Faso by intermediaries and recruiters to produce cocoa. Children from Cross River and Akwa Ibom states in southeastern Nigeria are particularly vulnerable. Some children are sold by their parents to recruiters. The recruiters are paid for their recruitment of the children; many children receive no pay for their work. Some children are forced to work long hours, including during the hottest hours of the day, leaving them at substantial risk for heat-related illness. The children are forced to perform dangerous tasks, such as using sharp tools, carrying heavy loads, and handling pesticides, without protective equipment. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Sierra Leone | Child Labor | |
| Côte d'Ivoire | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple cocoa and chocolate products made in Côte d’Ivoire are produced with an input made with child labor, specifically from cocoa beans produced in Côte d’Ivoire. These products include cocoa paste, cocoa butter, cocoa powder, and chocolate. Cocoa from Côte d’Ivoire produced with child labor, forced labor, and forced child labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Based on the most recently available estimate from NORC at the University of Chicago, the prevalence rate of child labor in cocoa production among cocoa growing households is 41%, meaning about 790,000 children work in child labor in cocoa production in Côte d’Ivoire. These cocoa-growing households produce the vast majority Côte d’Ivoire’s cocoa beans. Thus, products that rely heavily on cocoa beans originating from Côte d’Ivoire are at high risk of having an input produced with child labor. In 2022, the Netherlands imported 39% of its cocoa beans, 62% of its cocoa paste, 33% of its cocoa butter, and 31% of its cocoa powder from Côte d’Ivoire, using these inputs to produce cocoa and chocolate products. The availability of continued research demonstrates the Government of Côte d’Ivoire’s commitment to addressing labor abuses in the cocoa industry. Nonetheless, the use of child labor in Côte d’Ivoire’s production of cocoa beans remains a significant challenge. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor |
| Ghana | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple cocoa and chocolate products made in Ghana are produced with an input made with child labor, specifically from cocoa beans produced in Ghana. These products include cocoa paste, cocoa butter, cocoa powder, and chocolate. Cocoa from Ghana produced with child labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Based on the most recently available estimate from NORC at the University of Chicago, the prevalence rate of child labor in cocoa production among cocoa growing households is 55%, meaning an estimated 765,754 children work in child labor in cocoa production in Ghana. These cocoa growing households produce the vast majority of Ghana’s cocoa beans. Thus, products that rely heavily on cocoa beans originating from Ghana are at risk of having an input produced with child labor. The availability of this research demonstrates the Government of Ghana’s commitment to addressing labor abuses in the cocoa industry. Nonetheless, the use of child labor in Ghana’s production of cocoa beans remains a significant challenge. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor |
| Netherlands | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple cocoa and chocolate products produced in the Netherlands are produced with an input produced with child labor, specifically from cocoa beans produced in Ghana and Côte |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor |
| Côte d'Ivoire | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple cocoa and chocolate products made in Côte d’Ivoire are produced with an input made with child labor, specifically from cocoa beans produced in Côte d’Ivoire. These products include cocoa paste, cocoa butter, cocoa powder, and chocolate. Cocoa from Côte d’Ivoire produced with child labor, forced labor, and forced child labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Based on the most recently available estimate from NORC at the University of Chicago, the prevalence rate of child labor in cocoa production among cocoa growing households is 41%, meaning about 790,000 children work in child labor in cocoa production in Côte d’Ivoire. These cocoa-growing households produce the vast majority Côte d’Ivoire’s cocoa beans. Thus, products that rely heavily on cocoa beans originating from Côte d’Ivoire are at high risk of having an input produced with child labor. In 2022, the Netherlands imported 39% of its cocoa beans, 62% of its cocoa paste, 33% of its cocoa butter, and 31% of its cocoa powder from Côte d’Ivoire, using these inputs to produce cocoa and chocolate products. The availability of continued research demonstrates the Government of Côte d’Ivoire’s commitment to addressing labor abuses in the cocoa industry. Nonetheless, the use of child labor in Côte d’Ivoire’s production of cocoa beans remains a significant challenge. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor |
| Ghana | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple cocoa and chocolate products made in Ghana are produced with an input made with child labor, specifically from cocoa beans produced in Ghana. These products include cocoa paste, cocoa butter, cocoa powder, and chocolate. Cocoa from Ghana produced with child labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Based on the most recently available estimate from NORC at the University of Chicago, the prevalence rate of child labor in cocoa production among cocoa growing households is 55%, meaning an estimated 765,754 children work in child labor in cocoa production in Ghana. These cocoa growing households produce the vast majority of Ghana’s cocoa beans. Thus, products that rely heavily on cocoa beans originating from Ghana are at risk of having an input produced with child labor. The availability of this research demonstrates the Government of Ghana’s commitment to addressing labor abuses in the cocoa industry. Nonetheless, the use of child labor in Ghana’s production of cocoa beans remains a significant challenge. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor |
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?