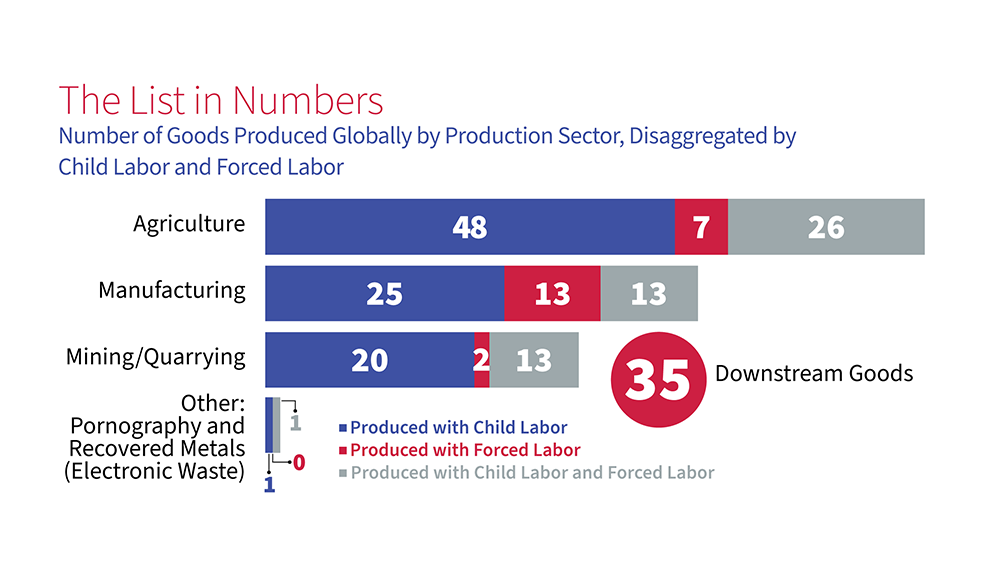
List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 204 goods from 82 countries and areas, as of September 5, 2024.
The Frederick Douglass Trafficking Victims Prevention and Protection Reauthorization Act of 2018 directs that the List include, "to the extent practicable, goods that are produced with inputs that are produced with forced labor or child labor."
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Previous TVPRA List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
2022
- List of Goods (Full Report) (PDF)
- List of Downstream Goods (Excel)
- List of Goods (Bibliography) (PDF)
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
DOL's mission is to foster, promote, and develop the welfare of the wage earners, job seekers, and retirees of the United States. This DOL mission is carried out by a variety of sub-agencies and offices (DOL agencies) covering domestic and international policy engagements, workforce development, enforcement, statistics, and benefits. DOL has a responsibility to protect the integrity of scientific information that is produced, communicated, and used across DOL agencies to better carry out its mission. ILAB is committed to using the highest possible scientific integrity and quality standards and practices to conduct our critical work. Scientific integrity is the adherence to professional practices, ethical behavior, and the principles of honesty and objectivity when conducting, managing, using the results of, and communicating about science and scientific activities. Inclusivity, transparency, and protection from inappropriate influence are hallmarks of scientific integrity.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Venezuela | There are reports that children as young as 9 years old work in the gold mines of Venezuela. Most of the gold mining in this sector takes place in a region in the south of the country known as the Orinoco Mining Arc. Due to their low weight and small build, children are often utilized in the extraction of the mineral from a network of small, unsupported caves. Children are also tasked with lowering people into the mines, and operating machinery such as electric hammers and gas extractors. These children work long hours, ranging from 10 to 15 hours a day, in dangerous conditions. Children working in this sector do so without access to toilets, safety equipment, first aid, ventilation, or adequate hydration. They run the risk of mining accidents, contracting malaria or mercury poisoning, or being victims of gang violence. Many mines in the region are run by gangs called sindicatos, and increasingly by armed groups such as FARC and ELN. These groups levy taxes and exercise strict control over these mining communities, often under threat of violence. Reports indicate that sometimes children are victims of shootouts between gangs, armed groups, and government forces vying for control of certain mining operations. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Zimbabwe | There are reports that children as young as 8 are engaged in the production of gold in Zimbabwe. Child labor occurs at unregulated artisanal and small-scale gold mining sites, including riverbeds in Mudzi and Mazowe. Sources estimated that thousands of children are working at gold mining sites and doing various work activities, including panning and sieving gold around riverbeds, digging and drilling in pit areas, and collecting and carrying gold ore. Children engaged in gold production in Zimbabwe work in hot climate conditions, lack proper protective equipment, and face exposure to dangerous chemicals, such as mercury. According to NGO reports, at least two children died during a mine shaft collapse. |
Child Labor |
| Burkina Faso | There are reports that children ages 5 to 17 work in granite quarries in Burkina Faso. These children are primarily found in granite quarries located in Pissy and Yagma, on the outskirts of the capital, Ouagadougou. According to Government of Burkina Faso officials, NGOs, and the U.S. Department of State, numerous incidents of child labor have been reported in these granite quarries, including hundreds of children working in the Pissy quarry, and NGOs report that the problem is increasing. Children work for long hours breaking large rocks by hand and carrying heavy loads of dirt, rock, and gravel. Children in granite quarries are at high risk of physical injury, and are exposed to large quantities of dust and smoke, which can cause respiratory diseases. Some children also experience physical abuse in the quarries. |
Child Labor |
| Nigeria | There are reports that children, mostly boys ages 4-17, are forced to quarry granite in Nigeria. Some children are abducted and trafficked from within Nigeria and from Benin to work in granite quarries and mines in the Federal Capital Territory, as well as the states of Ebonyi, Enugu, Ogun, Oyo, and Osun. Reports from the United Nations (UN) and media indicate that between 5,000 and 6,000 children from Benin alone were forced to work in the granite quarries; multiple government rescue operations identified between 50 and 200 children engaged in this work at a time. The children are forced to work up to 16 hours a day, even when they are sick. Many are forced to work under threat of physical violence. Children are often forced to sleep outside and are denied food. Reports indicate that children frequently die while working, having been forced to work under extreme conditions. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Sierra Leone | Child Labor | |
| Benin | Child Labor | |
| Argentina | Child Labor | |
| Colombia | There is evidence that children between the ages of 5 and 14 work in the harvesting and production of grapes in Colombia. Based on an analysis of the Colombia Great Household Survey – Child Labor Module, an estimated 31,834 children under the minimum age for work are involved in child labor in the harvesting and production of grapes. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Colombia’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgment that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Guatemala | Child Labor | |
| Nicaragua | Child Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?