List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 204 goods from 82 countries and areas, as of September 5, 2024.
The Frederick Douglass Trafficking Victims Prevention and Protection Reauthorization Act of 2018 directs that the List include, "to the extent practicable, goods that are produced with inputs that are produced with forced labor or child labor."
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Previous TVPRA List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
2022
- List of Downstream Goods (Excel)
- List of Goods (Bibliography) (PDF)
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
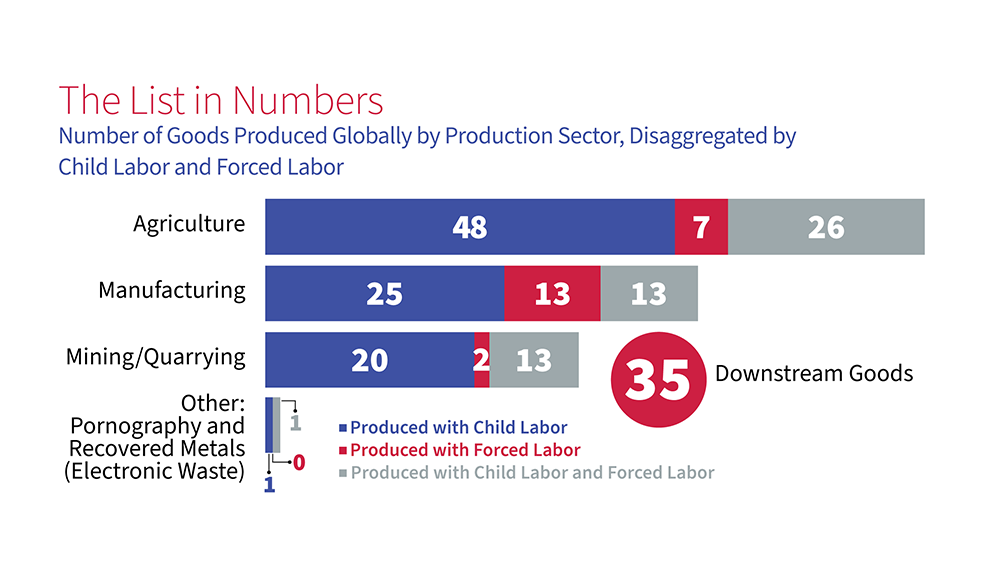
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
DOL's mission is to foster, promote, and develop the welfare of the wage earners, job seekers, and retirees of the United States. This DOL mission is carried out by a variety of sub-agencies and offices (DOL agencies) covering domestic and international policy engagements, workforce development, enforcement, statistics, and benefits. DOL has a responsibility to protect the integrity of scientific information that is produced, communicated, and used across DOL agencies to better carry out its mission. ILAB is committed to using the highest possible scientific integrity and quality standards and practices to conduct our critical work. Scientific integrity is the adherence to professional practices, ethical behavior, and the principles of honesty and objectivity when conducting, managing, using the results of, and communicating about science and scientific activities. Inclusivity, transparency, and protection from inappropriate influence are hallmarks of scientific integrity.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| China | There are reports that adults in China are forced to produce aluminum used in manufactured goods. Reports indicate that Uyghurs, ethnic Kazakhs, and other Muslim minorities from the XUAR are frequently subjected to forced labor in China through state-sponsored labor transfer programs. The Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (XPCC) is a government paramilitary organization in Xinjiang that runs labor transfer programs and owns aluminum companies. There is evidence that both XPCC and non-XPCC aluminum producers in Xinjiang have received hundreds of members of persecuted groups through labor transfer programs. Academic researchers, media, and think tanks report that companies and government entities frequently engage in coercive recruitment, limit workers’ freedom of movement and communication, and subjected workers to constant surveillance, exclusion from community and social life, physical violence, and threats to family members. |
Forced Labor |
| China | Aluminum from China produced with forced labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2024. There are reports that adults in China are forced to produce aluminum used in manufactured goods. Reports indicate that Uyghurs, ethnic Kazakhs, and other Muslim minorities from the XUAR are frequently subjected to forced labor in China through state-sponsored labor transfer programs. The Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (XPCC) is a government paramilitary organization in Xinjiang that runs labor transfer programs and owns aluminum companies. There is evidence that both XPCC and non-XPCC aluminum producers in Xinjiang have received hundreds of members of persecuted groups through labor transfer programs. Labor transfers of this kind are undertaken involuntarily in the broader context of constant surveillance and under menace of penalty, including explicit and implicit threats of detention and internment and threats to family members. Sources indicate that approximately 17- 20% of China’s aluminum is manufactured in Xinjiang under these labor conditions. Aluminum from Xinjiang is used to produce aluminum-intensive auto parts in China, including parts of auto bodies, and auto-part components, including engine block alloy, aluminum sheet and aluminum coil, and aluminum wheel and chassis components. In 2022, China was the world’s largest aluminum manufacturer and the second-largest autoparts supplier to the U.S. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| China | There are reports that children, ages 8-17, are forced to produce bricks in China, with concentrations in the Shanxi and Henan provinces. Victims are from provinces across China; some children are abducted or trafficked through coercion and sold to work in brick kilns. Information from media sources and a research study indicate that the children are forced to work without pay under threat of physical violence, held against their will, watched by guards, and denied sufficient food. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| China | There are reports that adults are forced to produce caustic soda in China. Caustic soda has a wide variety of uses in industrial processes, including as an input to cleaning products and refining in mining activities. Research indicates that Uyghurs, ethnic Kazakhs, and other Muslim minorities from the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region (XUAR) are frequently subjected to forced labor as a result of state-sponsored labor transfer programs. Workers, often from poor rural areas, have been placed in factories in industrial areas within the XUAR, and have also been transferred to factories in other parts of China. China is the world’s largest producer of caustic soda, and approximately 16% of China’s production is based in Xinjiang. Caustic soda manufacturers work with the Chinese government to make use of ethnic minority groups for exploitative labor, often receiving financial incentives. Academic researchers, media, and think tanks report that companies and government entities frequently engage in coercive recruitment, limit workers’ freedom of movement and communication, and subjected workers to constant surveillance, religious retribution, exclusion from community and social life, physical violence, and threats to family members. |
Forced Labor |
| China | There are reports that children are forced to pick cotton in China. Reports from an NGO and the U.S. Government indicate that children in the Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region and in Gansu province are mobilized through schools and required by provincial regulations to work during the autumn harvest. According to the most recently available estimates, between 40,000 and 1 million students are mobilized annually for the harvest, beginning as early as the third grade. Most children are paid little if at all, after deductions for meals, transportation, and payments to the school. These students are required to pick daily quotas of cotton or pay fines, and performance in the cotton harvest is assessed for the students' promotion to higher grade levels. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| China | ILAB has reason to believe that electrolytic copper products and lithium-ion batteries produced in China are made with an input produced with child labor, specifically copper ore produced in the DRC. Copper ore from the DRC was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009 for child labor. Children mine, collect, crush, and wash copper ore in the DRC’s artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) sector in Haut-Katanga and Lualaba. This ore is sold and traded to processing facilities in the DRC, where copper ore mined by children becomes mixed with copper ore from a variety of sources. In 2021 and 2022, China imported over 63% of DRC’s copper—some of which was produced with copper ore mined by children— for further refining and use in a variety of electrolytic (high purity) copper products including wires, bars, billets, plates, pipes, tubes, foil, and fittings. Electrolytic copper and copper alloys are used to produce lithium-ion batteries in China. This research suggests that further downstream products of copper ore, such as electric vehicles, electrical equipment, electrical wiring, brass, steel, telecommunications products, and construction materials, may be produced with an input produced with child labor. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor |
| China | There are reports that children ages 13-15 are forced to produce electronics in China. Based on the most recently available data from media sources, government raids, and NGOs, hundreds of cases of forced child labor have been reported in factories in Guangdong province, but the children are often from Henan, Shanxi, or Sichuan provinces. In some cases, children are forced to work in electronics factories through arrangements between the factories and the schools that the children attend in order to cover alleged tuition debts. The forced labor programs are described as student apprenticeships; however, the children report that they were forced to remain on the job and not allowed to return home. Half of the students' wages are sent directly to the schools, and the children receive little compensation after deductions are made for food and accommodations. In other cases, children are abducted or deceived by recruiters, sent to Guangdong, and sold to employers. Some children are held captive, forced to work long hours for little pay. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| China | There are reports that adults are forced to work in the production of fish on China’s distant-water fishing fleet. China’s fleet is the largest in the world, with an estimated 3,000 fishing vessels, and contains a wide variety of vessels, from longliners to purse seiners, operating on the high seas and in foreign countries’ exclusive economic zones in every region of the world. The majority of the crew on board are migrant workers from Indonesia and the Philippines, who are particularly vulnerable to forced labor. It is estimated that there are tens of thousands of workers who are sometimes recruited by agencies that deceive workers with false information regarding their wages and the terms of the contracts, and require the workers to pay recruitment fees and sign debt contracts. According to various sources, numerous incidents of forced labor have been reported on Chinese fishing vessels. While on board the vessels, workers’ identity documents are often confiscated, the crew spends months at sea without stopping at a port of call, and they are forced to work 18 to 22 hours a day with little rest. Workers face hunger and dehydration, live in degrading and unhygienic conditions, are subjected to physical violence and verbal abuse, are prevented from leaving the vessel or ending their contracts, and are frequently not paid their promised wages. |
Forced Labor |
| China | ILAB has reason to believe that cotton thread/yarn, cotton textiles, and cotton garments produced in China are made with an input produced with forced labor—specifically cotton harvested in China. Cotton from China is on ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor for forced labor, child labor, and forced child labor. About 85% of China’s cotton and 20% of the world’s cotton is produced in the XUAR, where research has shown it is harvested and processed under conditions of forced labor. In China, this cotton is spun into cotton thread/yarn and textiles and may be mixed with cotton from other sources. Manufacturers in China source large volumes of cotton fabrics containing Xinjiang origin cotton to produce finished garments. It is likely that products of Xinjiang-origin cotton produced further downstream, such as garments, textiles, and other cotton-based products, may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Forced Labor, Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Vietnam | ILAB has reason to believe that cotton garments produced in Vietnam are made with an input produced with forced labor, specifically cotton harvested in China. Cotton from China is on ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor for forced labor, child labor, and forced child labor. About 85% of China’s cotton and 20% of the world’s cotton is produced in the XUAR, where research has shown it is harvested and processed under conditions of forced labor. In China, this cotton is spun into cotton thread/yarn and textiles and may be mixed with cotton from other sources. Manufacturers in Vietnam source large volumes of cotton fabrics containing Xinjiang-origin cotton to produce finished garments. For example, in 2021 Vietnam imported 70% of its cotton-containing textiles from China ($2.6 billion). It is likely that further downstream products of Xinjiang-origin cotton, such as garments, textiles, and other cotton-based products, may be produced with an input produced with forced labor.
|
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?