List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 204 goods from 82 countries and areas, as of September 5, 2024.
The Frederick Douglass Trafficking Victims Prevention and Protection Reauthorization Act of 2018 directs that the List include, "to the extent practicable, goods that are produced with inputs that are produced with forced labor or child labor."
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Previous TVPRA List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
2022
- List of Downstream Goods (Excel)
- List of Goods (Bibliography) (PDF)
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
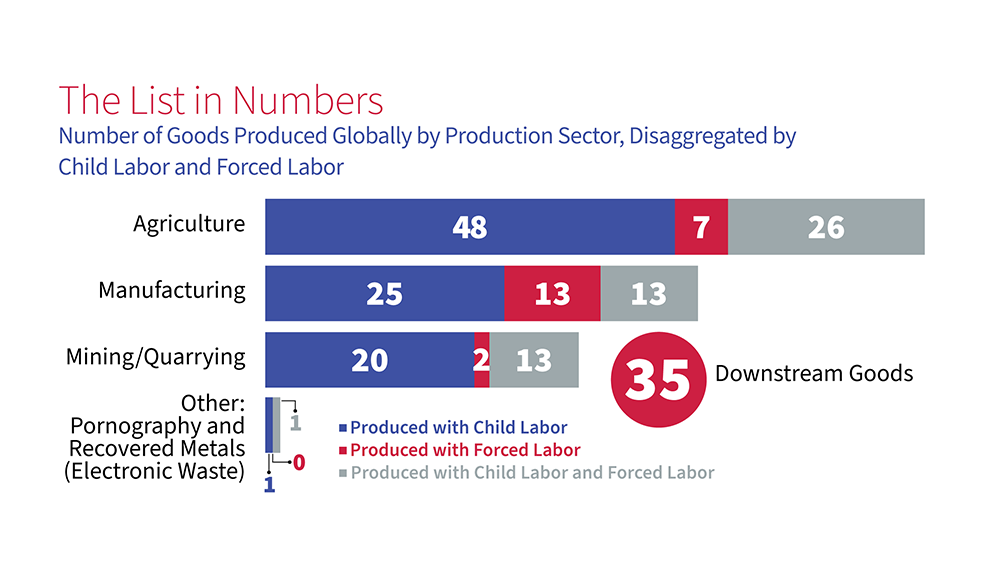
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
DOL's mission is to foster, promote, and develop the welfare of the wage earners, job seekers, and retirees of the United States. This DOL mission is carried out by a variety of sub-agencies and offices (DOL agencies) covering domestic and international policy engagements, workforce development, enforcement, statistics, and benefits. DOL has a responsibility to protect the integrity of scientific information that is produced, communicated, and used across DOL agencies to better carry out its mission. ILAB is committed to using the highest possible scientific integrity and quality standards and practices to conduct our critical work. Scientific integrity is the adherence to professional practices, ethical behavior, and the principles of honesty and objectivity when conducting, managing, using the results of, and communicating about science and scientific activities. Inclusivity, transparency, and protection from inappropriate influence are hallmarks of scientific integrity.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| India | Embellished Textiles There are reports of children, many between the ages of 8-14, producing embellished textiles under conditions of forced labor in India. Some children work under a system of debt bondage. Most factories that produce zari, a type of embroidery, are concentrated in Mumbai and Delhi, but many children are trafficked from other locations such as Bihar. According to government raids and an NGO report, between 125,000 and 210,000 children are working in Delhi embroidery workshops, and approximately 100,000 are working in zari embroidery and other textile embellishment workshops in Mumbai and elsewhere. Some children are forced to work under threat of physical violence. Some work long hours including overtime and do not receive payment for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Nepal | Embellished Textiles There are reports that children, mostly boys ages 7-17, are forced to produce embellished textiles in Nepal. The factories are spread across the Kathmandu Valley and are concentrated in Thankot. The child workers are mainly recruited from Sarlahi, Mohattari, and Dhanusha Districts. Based on a research report, close to 7,500 children are working under forced labor conditions in the sector. Factory owners often recruit certain boys to work on one- or two-year contracts, paying an advance to their parents for the boys' labor. The boys are forced to work long hours without pay. At the end of the contract, the factory owner offers another advance payment to the parents, and the boys then return to work for the factory. During the subsequent contract, the children receive little or no wages after the initial advance payment as wages are deducted to repay the advance, and accommodation and food expenses are also deducted. These children live at the worksite, and the factories are often locked, preventing the children from leaving. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| China | Garments ILAB has reason to believe that cotton thread/yarn, cotton textiles, and cotton garments produced in China are made with an input produced with forced labor—specifically cotton harvested in China. Cotton from China is on ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor for forced labor, child labor, and forced child labor. About 85% of China’s cotton and 20% of the world’s cotton is produced in the XUAR, where research has shown it is harvested and processed under conditions of forced labor. In China, this cotton is spun into cotton thread/yarn and textiles and may be mixed with cotton from other sources. Manufacturers in China source large volumes of cotton fabrics containing Xinjiang origin cotton to produce finished garments. It is likely that products of Xinjiang-origin cotton produced further downstream, such as garments, textiles, and other cotton-based products, may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Forced Labor, Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Vietnam | Garments Cotton ILAB has reason to believe that cotton garments produced in Vietnam are made with an input produced with forced labor, specifically cotton harvested in China. Cotton from China is on ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor for forced labor, child labor, and forced child labor. About 85% of China’s cotton and 20% of the world’s cotton is produced in the XUAR, where research has shown it is harvested and processed under conditions of forced labor. In China, this cotton is spun into cotton thread/yarn and textiles and may be mixed with cotton from other sources. Manufacturers in Vietnam source large volumes of cotton fabrics containing Xinjiang-origin cotton to produce finished garments. For example, in 2021 Vietnam imported 70% of its cotton-containing textiles from China ($2.6 billion). It is likely that further downstream products of Xinjiang-origin cotton, such as garments, textiles, and other cotton-based products, may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Bangladesh | Jute (textiles) | Child Labor |
| Bangladesh | Textiles | Child Labor |
| Cambodia | Textiles | Child Labor |
| China | Textiles ILAB has reason to believe that cotton thread/ yarn, cotton textiles, and cotton garments produced in China are made with an input produced with forced labor—specifically cotton harvested in China. Cotton from China is on ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor for forced labor, child labor, and forced child labor. About 85% of China’s cotton and 20% of the world’s cotton is produced in the XUAR, where research has shown it is harvested and processed under conditions of forced labor. In China, this cotton is spun into cotton thread/yarn and textiles and may be mixed with cotton from other sources. Manufacturers in China source large volumes of cotton fabrics containing Xinjiang origin cotton to produce finished garments. It is likely that products of Xinjiang-origin cotton produced further downstream, such as garments, textiles, and other cotton-based products, may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor, Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Ghana | Textiles There is evidence that children ages 5 to 14 are involved in the weaving of textiles in Ghana. Based on an analysis of the Ghana Living Standards Survey, an estimated 23,856 child laborers are involved in the weaving of textiles. There are numerous health and safety issues associated with the textile industry. These hazards include chemical exposure from the processing and dyeing of materials, exposure to cotton and other organic dusts, musculoskeletal stresses, and noise exposure. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Ghana’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Korea, North | Textiles | Forced Labor |
| Pakistan | Textiles There is evidence that children under 14 work in the production of textiles in Pakistan. Based on an analysis of the Pakistan Labour Force Survey 2017– 2018, an estimated 45,699 children are involved in child labor in the production of textiles. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Pakistan’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgment that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Vietnam | Textiles There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 in Vietnam produce textiles. Based on the Government of Vietnam’s National Child Labor Survey 2012, the results of which were published in 2014, an estimated 6,049 child laborers work in textile production, mainly in the fabrication and finishing stages of the process. About 42.9 percent, or 2,595, of these child laborers are under 15 years old, which is the minimum age for employment in Vietnam. Of the estimated 6,049 child laborers who produce textiles, about 448 are 5-11 years old, 2,147 are 12-14 years old, and 3,454 are 15-17 years old. Approximately 96 percent of child textile workers are female. The survey considers a child to be engaged in child labor if the child is working an excessive number of hours per week for his or her age, or if the child is engaged in work that is prohibited for underage employees according to national legislation. |
Child Labor |
| Ethiopia | Textiles (hand-woven) There are reports that children, mostly boys as young as seven years old, produce woven textiles under conditions of forced labor in Ethiopia. These children typically work in Addis Ababa, however many come from the south, including Gamo Gofa and Wolaita zones, some of them as victims of trafficking. The trafficked children are often sold to recruiters, and the parents and children are deceived with false promises about the wages and opportunities for education while working. Some of the children sleep at the worksites, held in captivity and isolation, and are not provided with sufficient food. They are punished with physical abuse. Some children are forced to work long hours and overtime, and receive little, if any, pay. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| China | Thread/Yarn ILAB has reason to believe that cotton thread/ yarn, cotton textiles, and cotton garments produced in China are made with an input produced with forced labor—specifically cotton harvested in China. Cotton from China is on ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor for forced labor, child labor, and forced child labor. About 85% of China’s cotton and 20% of the world’s cotton is produced in the XUAR, where research has shown it is harvested and processed under conditions of forced labor. In China, this cotton is spun into cotton thread/yarn and textiles and may be mixed with cotton from other sources. Manufacturers in China source large volumes of cotton fabrics containing Xinjiang origin cotton to produce finished garments. It is likely that products of Xinjiang-origin cotton produced further downstream, such as garments, textiles, and other cotton-based products, may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Forced Labor, Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?