List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 204 goods from 82 countries and areas, as of September 5, 2024.
The Frederick Douglass Trafficking Victims Prevention and Protection Reauthorization Act of 2018 directs that the List include, "to the extent practicable, goods that are produced with inputs that are produced with forced labor or child labor."
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Previous TVPRA List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
2022
- List of Downstream Goods (Excel)
- List of Goods (Bibliography) (PDF)
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
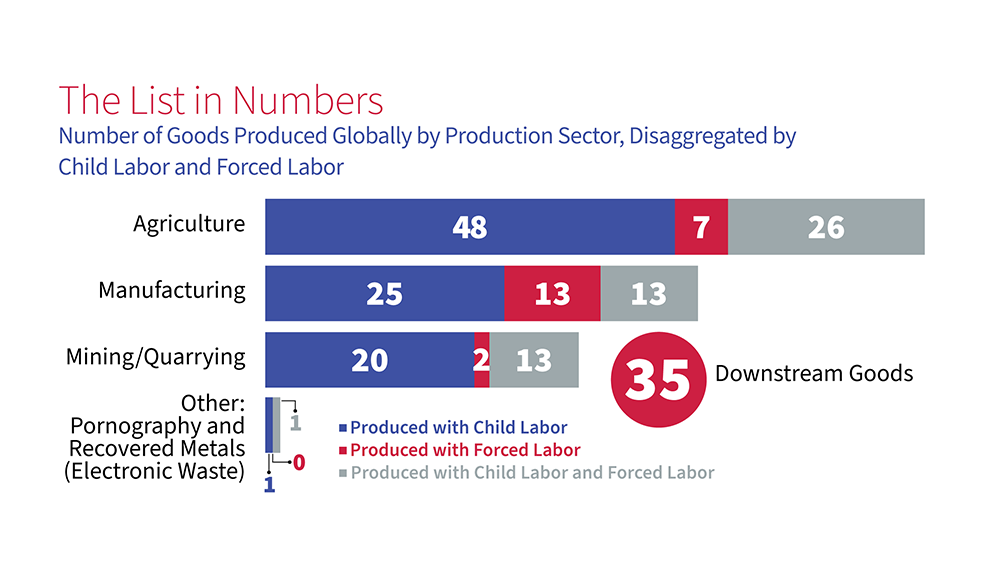
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
DOL's mission is to foster, promote, and develop the welfare of the wage earners, job seekers, and retirees of the United States. This DOL mission is carried out by a variety of sub-agencies and offices (DOL agencies) covering domestic and international policy engagements, workforce development, enforcement, statistics, and benefits. DOL has a responsibility to protect the integrity of scientific information that is produced, communicated, and used across DOL agencies to better carry out its mission. ILAB is committed to using the highest possible scientific integrity and quality standards and practices to conduct our critical work. Scientific integrity is the adherence to professional practices, ethical behavior, and the principles of honesty and objectivity when conducting, managing, using the results of, and communicating about science and scientific activities. Inclusivity, transparency, and protection from inappropriate influence are hallmarks of scientific integrity.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| Dominican Republic | Bagasse ILAB has reason to believe that raw sugar, refined sugar, molasses, rum, bagasse, and furfural produced in the Dominican Republic (DR) are produced with an input produced with forced labor, specifically sugarcane produced in the DR. Sugarcane from the DR produced with forced labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Numerous reports indicate the widespread presence of forced labor throughout the sugarcane sector of the DR, including in plantations owned by private companies, state-owned entities, and small independent producers (colonos). Sugarcane workers in the DR, particularly workers of Haitian origin or descent, work and live under conditions of forced labor. Sugarcane is used to produce a number of sugar-based products in the DR. The U.S. imports nearly all the raw sugar and the majority of the molasses exported from the DR, while the EU imports all of the produced furfural. In 2023, the U.S. imported over $131 million in raw sugar from the DR. Research suggests that further downstream products of sugarcane, such as beverages, alcoholic beverages, candy, baked goods, processed food products, animal feed, paper, pulp, construction materials, biofuels, industrial chemicals, medicines, and medicinal alcohol may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Dominican Republic | Furfural ILAB has reason to believe that raw sugar, refined sugar, molasses, rum, bagasse, and furfural produced in the Dominican Republic (DR) are produced with an input produced with forced labor, specifically sugarcane produced in the DR. Sugarcane from the DR produced with forced labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Numerous reports indicate the widespread presence of forced labor throughout the sugarcane sector of the DR, including in plantations owned by private companies, state-owned entities, and small independent producers (colonos). Sugarcane workers in the DR, particularly workers of Haitian origin or descent, work and live under conditions of forced labor. Sugarcane is used to produce a number of sugar-based products in the DR. The U.S. imports nearly all the raw sugar and the majority of the molasses exported from the DR, while the EU imports all of the produced furfural. In 2023, the U.S. imported over $131 million in raw sugar from the DR. Research suggests that further downstream products of sugarcane, such as beverages, alcoholic beverages, candy, baked goods, processed food products, animal feed, paper, pulp, construction materials, biofuels, industrial chemicals, medicines, and medicinal alcohol may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Dominican Republic | Molasses ILAB has reason to believe that raw sugar, refined sugar, molasses, rum, bagasse, and furfural produced in the Dominican Republic (DR) are produced with an input produced with forced labor, specifically sugarcane produced in the DR. Sugarcane from the DR produced with forced labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Numerous reports indicate the widespread presence of forced labor throughout the sugarcane sector of the DR, including in plantations owned by private companies, state-owned entities, and small independent producers (colonos). Sugarcane workers in the DR, particularly workers of Haitian origin or descent, work and live under conditions of forced labor. Sugarcane is used to produce a number of sugar-based products in the DR. The U.S. imports nearly all the raw sugar and the majority of the molasses exported from the DR, while the EU imports all of the produced furfural. In 2023, the U.S. imported over $131 million in raw sugar from the DR. Research suggests that further downstream products of sugarcane, such as beverages, alcoholic beverages, candy, baked goods, processed food products, animal feed, paper, pulp, construction materials, biofuels, industrial chemicals, medicines, and medicinal alcohol may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Dominican Republic | Raw Sugar ILAB has reason to believe that raw sugar, refined sugar, molasses, rum, bagasse, and furfural produced in the Dominican Republic (DR) are produced with an input produced with forced labor, specifically sugarcane produced in the DR. Sugarcane from the DR produced with forced labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Numerous reports indicate the widespread presence of forced labor throughout the sugarcane sector of the DR, including in plantations owned by private companies, state-owned entities, and small independent producers (colonos). Sugarcane workers in the DR, particularly workers of Haitian origin or descent, work and live under conditions of forced labor. Sugarcane is used to produce a number of sugar-based products in the DR. The U.S. imports nearly all the raw sugar and the majority of the molasses exported from the DR, while the EU imports all of the produced furfural. In 2023, the U.S. imported over $131 million in raw sugar from the DR. Research suggests that further downstream products of sugarcane, such as beverages, alcoholic beverages, candy, baked goods, processed food products, animal feed, paper, pulp, construction materials, biofuels, industrial chemicals, medicines, and medicinal alcohol may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Dominican Republic | Refined Sugar ILAB has reason to believe that raw sugar, refined sugar, molasses, rum, bagasse, and furfural produced in the Dominican Republic (DR) are produced with an input produced with forced labor, specifically sugarcane produced in the DR. Sugarcane from the DR produced with forced labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Numerous reports indicate the widespread presence of forced labor throughout the sugarcane sector of the DR, including in plantations owned by private companies, state-owned entities, and small independent producers (colonos). Sugarcane workers in the DR, particularly workers of Haitian origin or descent, work and live under conditions of forced labor. Sugarcane is used to produce a number of sugar-based products in the DR. The U.S. imports nearly all the raw sugar and the majority of the molasses exported from the DR, while the EU imports all of the produced furfural. In 2023, the U.S. imported over $131 million in raw sugar from the DR. Research suggests that further downstream products of sugarcane, such as beverages, alcoholic beverages, candy, baked goods, processed food products, animal feed, paper, pulp, construction materials, biofuels, industrial chemicals, medicines, and medicinal alcohol may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Dominican Republic | Rum ILAB has reason to believe that raw sugar, refined sugar, molasses, rum, bagasse, and furfural produced in the Dominican Republic (DR) are produced with an input produced with forced labor, specifically sugarcane produced in the DR. Sugarcane from the DR produced with forced labor was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009. Numerous reports indicate the widespread presence of forced labor throughout the sugarcane sector of the DR, including in plantations owned by private companies, state-owned entities, and small independent producers (colonos). Sugarcane workers in the DR, particularly workers of Haitian origin or descent, work and live under conditions of forced labor. Sugarcane is used to produce a number of sugar-based products in the DR. The U.S. imports nearly all the raw sugar and the majority of the molasses exported from the DR, while the EU imports all of the produced furfural. In 2023, the U.S. imported over $131 million in raw sugar from the DR. Research suggests that further downstream products of sugarcane, such as beverages, alcoholic beverages, candy, baked goods, processed food products, animal feed, paper, pulp, construction materials, biofuels, industrial chemicals, medicines, and medicinal alcohol may be produced with an input produced with forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Turkey (Türkiye) | Sugar Beets | Child Labor |
| Belize | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Bolivia | Sugarcane There are reports that children are forced to produce sugarcane in Bolivia. Based on the most recently available data from the ILO, it is estimated that almost a quarter of the migrants working in the sugarcane harvest are children under age 14, of which many are working in conditions of forced labor Many children work with their families under conditions of bonded labor. Entire families, including children, live in accommodations provided by the employer; this dependence on the employer increases their vulnerability to forced labor. The families receive little payment if any, and lodging and food expenses are deducted from their paychecks. Some children inherit the debt of their parents if their parents pass away or stop working, and remain bonded and able to be sold to a different employer. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Brazil | Sugarcane There is evidence that children ages 14 to 17 cultivate sugarcane in Brazil. Brazilian law prohibits all children under age 18 from producing sugarcane. Based on an analysis of the Government of Brazil’s 2015 National Household Survey, an estimated 5,503 child laborers cultivate sugarcane. Individuals, including children, who work in sugarcane production are exposed to long hours and high temperatures, and lack protective equipment. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Brazil’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgement that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Burma | Sugarcane There are reports that children are forced to work in the production of sugarcane in Burma. Forced child labor is found in the Thaton District, and particularly in areas near military camps. An NGO study documents villagers, including children, mobilized by the dozens each day from multiple villages to work during labor intensive times of the sugarcane production. The children are forced to cut trees and dig out the stumps to prepare the fields, plant the sugarcane, then mill and boil the sugarcane after it is harvested. They are not paid for their work. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Cambodia | Sugarcane There are reports that children ages 5 to 17 produce sugarcane in Cambodia. Child labor in the sugarcane sector occurs on both commercial plantations and smallholder farms. Children from families that have lost land through concessions to sugar companies are particularly vulnerable to exploitative labor on plantations. According to international organizations, NGOs, and media reports, child labor in the Cambodian sugarcane sector is a widespread concern, with numerous incidents reported across the country, including reports of hundreds of children cutting cane on plantations in the Koh Kong province. Children laboring in the sugarcane fields often work long hours under the hot sun and report difficulty breathing, headaches, and dizziness as a result. Child workers in this sector perform hazardous tasks such as carrying heavy bundles of sugarcane, using dangerous tools, and spraying toxic pesticides. Many children incur injuries on the job, including skin infections and cuts from sharp cane leaves or knives. |
Child Labor |
| Colombia | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Dominican Republic | Sugarcane There are reports that adults are forced to work in the harvesting and production of sugarcane in the Dominican Republic. These adults, the majority of whom are undocumented or stateless, are predominantly of Haitian origin or descent. Reports from civil society organizations, news media, worker interviews, field research, and other sources indicate the existence of the following forced labor indicators in the sugarcane sector: withholding of wages, abusive working and living conditions, excessive overtime, isolation and restriction of movement, and deceptive recruitment practices. For some workers, a precarious legal status and lack of identity documents limit their movement and have led to isolation and fears of reprisal, denouncement to authorities, loss of company-provided housing and deportation for complaining about unlawful labor conditions. In addition, illiteracy, low levels of education, and language barriers can impede their understanding and exercising of labor rights, thus increasing their vulnerability to labor exploitation. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| El Salvador | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Guatemala | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| India | Sugarcane Research found that sugarcane in India, especially sugarcane harvested in Maharashtra, is harvested using forced labor of adults. Workers in the sugarcane fields face excessive and involuntary overtime, severe and unexplained wage deductions, and degrading living conditions. They are commonly recruited against a debt, often resulting often in debt bondage. Women are frequently pressured into receiving unnecessary hysterectomies to avoid taking leave and missing harvesting quotas. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Kenya | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Mexico | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Pakistan | Sugarcane | Forced Labor |
| Paraguay | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Philippines | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Thailand | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Uganda | Sugarcane | Child Labor |
| Vietnam | Sugarcane There is evidence that children ages 5 to 17 grow sugarcane in Vietnam. The results of the Government of Vietnam’s National Child Labor Survey 2012, published in 2014, show that an estimated 28,303 child laborers are involved in growing sugarcane. Approximately 32.6 percent, or 9,227 of these child laborers are under 15 years old, which is the minimum age for employment in Vietnam. Of the estimated 28,303 child laborers who grow sugarcane, 3.9 percent are 5-11 years old, 28.7 percent are 12-14 years old, and 67.4 percent are 15-17 years old. The survey considers a child to be engaged in child labor if the child is working an excessive number of hours per week for his or her age, or if the child is engaged in work that is prohibited for underage employees according to national legislation. |
Child Labor |
| Zimbabwe | Sugarcane There are reports that children as young as age 9 produce sugarcane in Zimbabwe. Multiple local media reports identify cases of children working on sugarcane farms, particularly on outgrower farms in Masvingo Province, which is the main area for sugarcane cultivation in Zimbabwe. One source estimates that there are as many as 10,000 children working in the sector. Children working on farms producing sugarcane perform tasks related to irrigation, the cutting of sugarcane, and guarding crops. Children perform work at night and engage in hazardous activities, such as using machetes and chasing away wild animals. Many child laborers working in sugarcane production do not attend school because of their work. |
Child Labor |
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?