List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
The Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) maintains a list of goods and their source countries which it has reason to believe are produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards, as required under the Trafficking Victims Protection Reauthorization Act (TVPRA) of 2005 and subsequent reauthorizations. The List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor comprises 204 goods from 82 countries and areas, as of September 5, 2024.
The Frederick Douglass Trafficking Victims Prevention and Protection Reauthorization Act of 2018 directs that the List include, "to the extent practicable, goods that are produced with inputs that are produced with forced labor or child labor."
ILAB maintains the List primarily to raise public awareness about forced labor and child labor around the world and to promote efforts to combat them; it is not intended to be punitive, but rather to serve as a catalyst for more strategic and focused coordination and collaboration among those working to address these problems.
Previous TVPRA List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor
2022
- List of Goods (Full Report) (PDF)
- List of Downstream Goods (Excel)
- List of Goods (Bibliography) (PDF)
Publication of the List has resulted in new opportunities for ILAB to engage with foreign governments to combat forced labor and child labor. It is also a valuable resource for researchers, advocacy organizations and companies wishing to carry out risk assessments and engage in due diligence on labor rights in their supply chains.
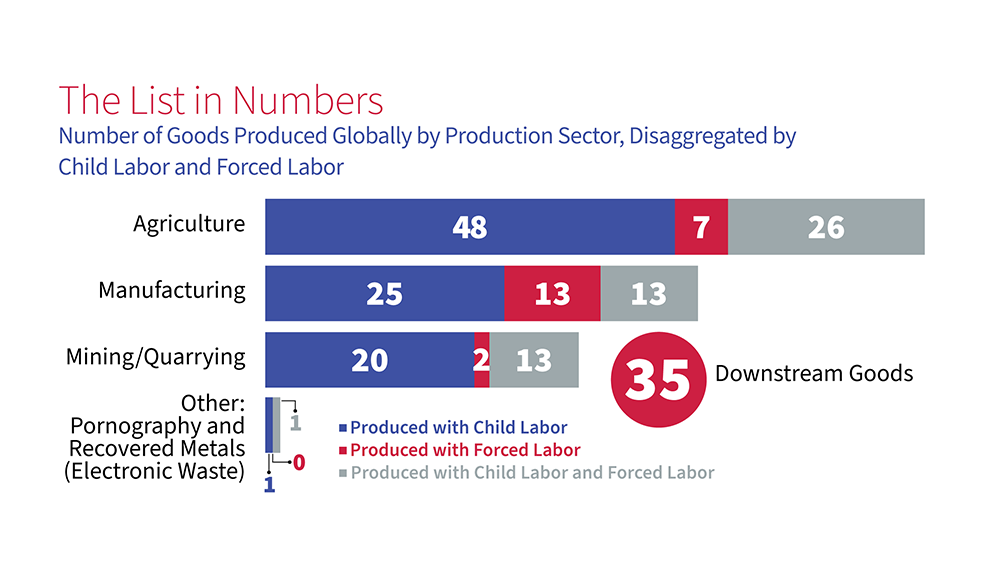
The countries on the List span every region of the world. The most common agricultural goods listed are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, tobacco, cattle, rice, and fish. In the manufacturing sector, bricks, garments, textiles, footwear, carpets, and fireworks appear most frequently. In mined or quarried goods, gold, coal and diamonds are most common.
ILAB published the initial TVPRA List in 2009 and updated it annually through 2014, following a set of procedural guidelines that were the product of an intensive public consultation process. ILAB now updates and publishes the List every other year, pursuant to changes in the law.
Procedural Guidelines
On January 25, 2024, ILAB's Office of Child Labor, Forced Labor, and Human Trafficking published Procedural Guidelines for the development and maintenance of the List of Goods from countries produced by child labor or forced labor in violation of international standards.
DOL's mission is to foster, promote, and develop the welfare of the wage earners, job seekers, and retirees of the United States. This DOL mission is carried out by a variety of sub-agencies and offices (DOL agencies) covering domestic and international policy engagements, workforce development, enforcement, statistics, and benefits. DOL has a responsibility to protect the integrity of scientific information that is produced, communicated, and used across DOL agencies to better carry out its mission. ILAB is committed to using the highest possible scientific integrity and quality standards and practices to conduct our critical work. Scientific integrity is the adherence to professional practices, ethical behavior, and the principles of honesty and objectivity when conducting, managing, using the results of, and communicating about science and scientific activities. Inclusivity, transparency, and protection from inappropriate influence are hallmarks of scientific integrity.
| Country/Area | Good | Exploitation Type |
|---|---|---|
| India | There are reports that children, especially girls ages 6-14, are forced to produce hybrid cottonseed in India. Cottonseed production, and cottonseed farms with bonded child laborers, are reported to be concentrated in the state of Andhra Pradesh. According to NGO reports, between 400,000 and 450,000 children are working in the production of hybrid cottonseed, many working as forced or bonded labor. Some of these children are bonded to their employer, forced to work to pay off the debt of advanced payments made to their parents. Some children are forced to work with toxic pesticides. |
Child Labor, Forced Labor |
| Indonesia | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple palm oil products produced in Indonesia are made with an input using child labor and forced labor, specifically palm fruit harvested in Indonesia. These palm oil products include crude palm oil, crude palm kernel oil, refined palm oil, refined palm kernel oil, and oleochemicals. Palm Fruit from Indonesia was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2010 for child labor and added in 2020 for forced labor. Indonesia produces most of the world’s palm fruit and palm oil. In 2020, refined palm oil from Indonesia accounted for 55.26 percent of global imports. In 2020, the U.S. obtained about 60 percent of its $1 billion in refined palm oil imports from Indonesia. This research suggests that further downstream products of palm fruit and palm oil, such as cooking oils, animal feed, bakery items and baked goods, beverages, household and industrial products, personal care and cosmetic products, infant formula, and biofuels, may be produced with an input produced with child labor and forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor, Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Malaysia | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple palm oil products produced in Malaysia are produced with an input derived from child labor and forced labor, specifically palm fruit produced in Malaysia. These palm oil products include crude palm oil, crude palm kernel oil, refined palm oil, refined palm kernel oil, cooking oil (palm oil blends), oleochemicals, and biofuel. Palm fruit from Malaysia was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009 for forced labor and added in 2014 for child labor. Research from NGOs and media reports continue to show tens of thousands of children work in the palm fruit sector in Malaysia. Similar reporting shows forced labor indicators are widespread in palm fruit plantations, particularly among migrant workers who face vulnerabilities during and after recruitment. This research suggests that further worldwide downstream products of palm fruit and palm oil, such as animal feed, baked goods, beverages, household and industrial products, personal care products, cosmetic products, infant formula, and shortening, may be produced with an input produced with child labor and forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor, Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Indonesia | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple palm oil products produced in Indonesia are made with an input using child labor and forced labor, specifically palm fruit harvested in Indonesia. These palm oil products include crude palm oil, crude palm kernel oil, refined palm oil, refined palm kernel oil, and oleochemicals. Palm Fruit from Indonesia was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2010 for child labor and added in 2020 for forced labor. Indonesia produces most of the world’s palm fruit and palm oil. In 2020, refined palm oil from Indonesia accounted for 55.26 percent of global imports. In 2020, the U.S. obtained about 60 percent of its $1 billion in refined palm oil imports from Indonesia. This research suggests that further downstream products of palm fruit and palm oil, such as cooking oils, animal feed, bakery items and baked goods, beverages, household and industrial products, personal care and cosmetic products, infant formula, and biofuels, may be produced with an input produced with child labor and forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor, Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Malaysia | ILAB has reason to believe that multiple palm oil products produced in Malaysia are produced with an input derived from child labor and forced labor, specifically palm fruit produced in Malaysia. These palm oil products include crude palm oil, crude palm kernel oil, refined palm oil, refined palm kernel oil, cooking oil (palm oil blends), oleochemicals, and biofuel. Palm fruit from Malaysia was added to ILAB’s List of Goods Produced by Child Labor or Forced Labor in 2009 for forced labor and added in 2014 for child labor. Research from NGOs and media reports continue to show tens of thousands of children work in the palm fruit sector in Malaysia. Similar reporting shows forced labor indicators are widespread in palm fruit plantations, particularly among migrant workers who face vulnerabilities during and after recruitment. This research suggests that further worldwide downstream products of palm fruit and palm oil, such as animal feed, baked goods, beverages, household and industrial products, personal care products, cosmetic products, infant formula, and shortening, may be produced with an input produced with child labor and forced labor. |
Inputs Produced with Child Labor, Inputs Produced with Forced Labor |
| Mexico | Child Labor | |
| Turkey (Türkiye) | Child Labor | |
| Pakistan | There is evidence that children under the age of 14 produce dairy products in Pakistan. An analysis of the Pakistan Labour Force Survey 2017–2018 considers all work performed by children under age 14 to be child labor. Based on an analysis of the survey, it is estimated that 81,375 child laborers produce dairy products. The ILO has found that generally, children who work with livestock may be at risk of exposure to hazards including working long hours, being injured by the animals, and exposure to the elements, diseases, and chemicals such as disinfectants. The release of this survey demonstrates the Government of Pakistan’s commitment to addressing child labor and its acknowledgment that data collection is vital to the design and implementation of sound policies and programs. |
Child Labor |
| Angola | Child Labor, Forced Labor | |
| Central African Republic | Child Labor |
your hand? Download ILAB's Sweat & Toil App today!
Are you a company looking to fight child labor and forced labor in supply
chains?